Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #7 Jewish versions

Leningrad Codex (cover page E, folio 474a)
The Leningrad Codex (Codex Leningradensis) or “L” is the oldest dated ms. of the complete Hebrew Bible, using the masoretic text and Tiberian vocalization. This earliest extant Hebrew Bible codex, Leningrad Codex or the Cairo Prophets was written and punctuated by Moses ben Asher in Tiberias (in Palestine) in 895. Next in age is the Leningrad Codex of the Latter Prophets dated to 916, which was not originally the work of Ben Asher, but its Babylonian pointing—i.e., vowel signs used for pronunciation purposes—was brought into line with the Tiberian Masoretic system.
Many wealthy Jews employed scribes to copy manuscripts in order to foster Bible study. When Abraham b. Ḥayyim di Tintori, a master craftsman had largely solved the problems of both vowel-points and accents it became easier to print Hebrew bibles.
Influenced of the Bibles and chronicles in rhyme produced by German writers from the ninth century onwards Yiddish bibles appeared in medieval times.
There are also rhymed Yiddish paraphrases of the Bible, which flourished in the 14th century, predating the rhymed translations. These paraphrases, unlike the translations, go beyond the original text and show the influence of German epic minstrelsy. The best-known work of this type is the socalled Shemuel Bukh, a rhymed paraphrase of I and II Samuel, the prototype of which appeared no later than about 1400, although the first printed edition is of a much later date (Augsburg, 1543). The Shemuel Bukh served as the model for a host of other biblical paraphrases in rhyme, including: three 14th-century paraphrases of Esther; one of Judges (14th–15th centuries); paraphrases of the five Megillot, which were apparently the work of Abraham b. Elijah of Vilna (15th–16th centuries); paraphrases of Judges and Isaiah by Moses b. Mordecai of Mantua (before 1511); and poetic reworkings of the account of the death of Moses and the Akedah. The last two display great originality, adorning the biblical stories with legendary motifs drawn from the midrashic aggadah, and endowing the biblical personalities and events described with medieval characteristics. By the 15th century there were also prose paraphrases of certain biblical books, most of which have, however, been lost. The existence of such literary works is indicated by the late 15th-century Ma’asiyyot (“tales”), stories in prose about the Akedah, Jonah, and King Solomon.
One of the most interesting rabbis of the Middle Ages, Rabbi Samuel (Shmu’el) son of (ben) Meir (Rashbam) of Northern France his writings were going to be used by many and it can be seen that many aspects of his Torah commentary seem similar to what we find in works of modern biblical scholarship.
For non Yiddish Jewish Bibles they first only saw prints in Hebrew, which started in a 1477 edition of the Psalms, with each verse followed by the appropriate passage from David Kimḥi‘s commentary, an arrangement which does not appear again in Hebrew Bibles. His dictionary of the Hebrew language called Sefer Hashorashim (Book of Roots) (ספר השורשים) draws heavily on the earlier works of Rabbi Judah ben David Hayyuj and Rabbi Jonah ibn Janah, as well as from the work of his father the grammarian, exegete, poet, and translator Rabbi Joseph Kimhi.
The first Great Rabbinic Bible, edited by Felix Pratensis, who was born a Jew but was baptized in 1506, was published in 1516–17.
From the early 18th century, progressive anglicization of Jewish settlers in England and America rendered first the Spanish, and ultimately the Yiddish, translations inadequate for educational needs. The King James Version became current in spite of the Christianizing tendency of some of its “headlines” to the Prophets. The Pentateuch with haftarot published in London by David Levi (1787) appears to be the King James Version but without offending captions and with Jewish annotations. An earlier Pentateuch was produced by A. Alexander in 1785.

Portrait of Seligman Baer, from the 1906 Jewish Encyclopedia.
The masoretic scholar Seligmann Baer, published an Hebrew Bible in single volumes with notes, except for Exodus to Deuteronomy, strictly following the Masoretic tradition. The volumes, with a Latin preface by Franz Delitzsch, appeared (Leipsic, Tauchnitz) in the following order: Genesis, 1869; Isaiah, 1872; Job, 1875; Minor Prophets, 1878; Psalms (together with a treatise “Elementa Accentuationis Metricæ”), 1880; Proverbs (together with “De Primorum Vocabulorum Dagessatione”), 1880; Daniel, Ezra, and Nehemiah (together with “Chaldaismi Biblici Adumbratio” and a treatise by Friedrich Delitzsch (son of Franz Delitzsch) on the Babylonian proper names in these books), were published in 1882; Ezekiel (with “Specimen Glossarii Ezechielico-Babylonici” by Friedrich Delitzsch), appeared in 1884; followed by the five Megillot, 1886; the book of Chronicles, 1888; Jeremiah, 1890; Joshua and Judges, 1891; and finally Kings, 1895. The last two were edited by Baer alone, Delitzsch having died in 1890.
Death prevented Baer from finishing the series. Attached to each volume were a number of Masoretic notes taken from the best editions and manuscripts, variant readings between the Occidentals and Orientals, between Ben Asher and Ben Naphtali, and various other Masoretic lists and enumerations.
The most comprehensive Polyglot Hebrew Bibles are Brian Walton‘s London Polyglot (1654–57) which contained texts in Hebrew, Samaritan, Aramaic, Greek, Latin, Ethiopic, Syriac, Arabic, and Persian (all with Latin translations), and Samuel Bagster‘s Polyglot (1831) in Hebrew, Greek, Samaritan, Latin, Syriac, German, Italian, French, English, and Spanish. More modern polyglots have contented themselves with giving the texts in Hebrew, Greek, Latin, and a modern language.
 Ashkenazi Jewish lay minister of religion, author, translator, editor, and publisher; pioneer of the Jewish pulpit in the United States, and founder Beth El Emeth synagogue and of the Jewish press of America, Isaac Leeser (1806–1868) who was well-grounded in Latin, German, and Hebrew and had also studied the Talmud tractates Moed, Bava Metzia, and portions of Kodashim and Bava Batra under Hebrew masters, made an effort to provide his fellow Jews in the New World with an English version of the Tanakh or Hebrew bible. He was the first Orthodox rabbi in America to break with European tradition and preach in English and wanted also the Torah in English.
Ashkenazi Jewish lay minister of religion, author, translator, editor, and publisher; pioneer of the Jewish pulpit in the United States, and founder Beth El Emeth synagogue and of the Jewish press of America, Isaac Leeser (1806–1868) who was well-grounded in Latin, German, and Hebrew and had also studied the Talmud tractates Moed, Bava Metzia, and portions of Kodashim and Bava Batra under Hebrew masters, made an effort to provide his fellow Jews in the New World with an English version of the Tanakh or Hebrew bible. He was the first Orthodox rabbi in America to break with European tradition and preach in English and wanted also the Torah in English.
This got him to present first the Pentateuch, Torat ha-Elohim (“The Torah of God”) in 1845 and then eight years later, adhering to the same Masoretic text that was used by the King James translators, he offered “The Twenty-four Books of the Holy Scriptures: Carefully Translated According to the Massoretic Text, On the Basis of the English Version, After the Best Jewish Authorities; and supplied with short explanatory notes. By Isaac Leeser. ” in Philadelphia, 1853. His complete Old Testament in English (1853) incorporated matter from the Mendelssohn school’s German translation and included the Hebrew text.
Criticism was that to much of the Teutonic protruded in the translation. His English being very Germanic, with long and complex sentences, but still the language of America.
On the other hand, the grammatical niceties of biblical Hebrew frequently came through successfully, and the scholarship in general was on a consistently adequate level. Leeser’s Bible would have retained much more of its deserved popularity well into the twentieth century — for it is generally superior even to such early twentieth-century authorized translations as the American Standard Version of 1901 (ASV)—had it not been for the appearance in 1917 of the translation sponsored by the Jewish Publication Society of America. {Harry Orlinski in his book Notes on the New Translation of the Torah (1969), p. 14}
This English Bible revision could be called “Jewish” in that it eliminates a few renderings that Jews have associated with Christianity (such as “virgin” in Isaiah 7:14 “young girl”), and also by virtue of its religious adherence to the traditional Hebrew text. Incorporating rabbinic readings of the Bible into his text via parentheses Leeser’s version stood as pre-eminent in the American Jewish community until the appearance of the “Old JPS” translation of 1917.
Leeser also believed in speaking to women, inspiring them, caring for their religious well-being. He wrote in The Occident:
The females, too, belong to Israel. And they also must be taught that they may understand and observe the law…. There is so much given to women, especially the women of Israel, that we may freely say with a great writer of modern days whose name we do not remember, ‘that we are always what women make us.’ When the child first begins to think, it is his mother who infuses in his mind the first ideas. It is his mother who teaches him to lisp the first words. If he is able to learn something of God, it is his mother again who instructs him to serve the great Being who is the creator of all. {Isaac Leeser: The Right Man at the Wrong Time}
After his death, Leeser’s publishing enterprise became the Jewish Publication Society, which still operates today. He was the forerunner of Artscroll, Koren and all the successful Orthodox publishers.
At the other site of the ocean in Great Britain Abraham Benisch the Bohemian journalist and theologian in pursuance of his mission, had came to London, where he devoted himself to Jewish journalism and literature, and acquired considerable influence in Jewish and Christian circles. he helped founding the Biblical Institute and its allies, The Syro-Egyptian and The Biblical Chronological societies. These three were afterwards fused into the Society of Biblical Archaeology. From from 1851 to 1861 in four sequential volumes he published A Translation of the Tanakh, Published with the Hebrew Text.
In 1896 C.G. Montefiore’s Bible for Home Reading was published.
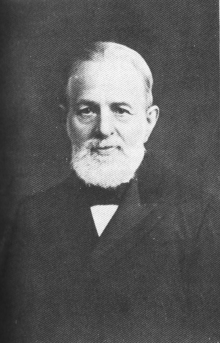
Michael Friedländer best known for his English translation from the original Arabic text of Maimonides’ Guide to the Perplexed.
Similar in style to the King James Version English Jewish people could find a Jewish Family Bible in English and Hebrew, edited by the orientalist and principal of Jews’ College, London, Michael Friedländer (1881).

After the Revised Version of 1885 had appeared, the London Jewish Religious Education Board published (1896) a pamphlet listing essential emendations to make that version acceptable for Jewish use. These modifications were among the material utilized for the version published by the Jewish Publication Society of America in 1917, which also took into account 19th-century Jewish Bible scholarship and rabbinical commentary (e.g., Malbim); the edition – issued by a committee representative of both traditional and Reform Judaism – was basically the work of Max L. Margolis.
The Central Conference of American Rabbis, the organization of Reform rabbis in 1892 brought a project to bring the first translation for which a group representing Jewish learning among English-speaking Jews assumed joint responsibility, but each person would take up a book to translate. Assigning different books of the Bible to individual rabbis and scholars did not look the ideal way to have a good progress. After more than a decade only the Book of Psalms had been sent to press. In 1908 the Jewish Publication Society of America agreed to take over the project. Under the direction of Editor-in-Chief Max Margolis, the editors included Solomon Schechter, Cyrus Adler, Joseph Jacobs, and faculty members of Hebrew Union College (associated with Reform Judaism), the Jewish Theological Seminary (part of the Conservative Judaism movement), and Dropsie College (a graduate school not affiliated with any movement).
They continued working on a version which essentially retained the Elizabethan diction. It stuck unswervingly to the received Hebrew text that it interpreted in accordance with Jewish tradition and the best scholarship of the day. For over half a century it remained authoritative, even though it laid no claim to any official ecclesiastical sanction.

The 1917 JPS translation.
The translation, which appeared in 1917, with the full publication title The Holy Scriptures According to the Masoretic Text: A New Translation with the Aid of Previous Versions and with Constant Consultation of Jewish Authorities, follows the edition of Seligman Baer except for the books of Exodus to Deuteronomy, which never appeared in Baer’s edition and for which C. D. Ginsburg‘s Hebrew text was used. It is heavily indebted to the Revised Version and American Standard Version.
The 1917 version is still widely disseminated through its appearance in the commentaries of the Soncino Books of the Bible, a set of Hebrew Bible commentaries, covering the whole Tanakh (Old Testament) in fourteen volumes, and the Torah commentary edited by Joseph H. Hertz. Further, it has influenced many subsequent 20th century translations by drawing attention to the Jewish view of many passages.

U.S. Jewish Zionist leader and founder of Hadassah, the Women’s Zionist Organization of America Henrietta Szold
In 1955 a renewed look at the Holy Scriptures from the Jewish view and tradition was taken. Reform Rabbi Joseph Krauskopf as a non-profit publisher got the daughter of the German-speaking Hungarian immigrant family of rabbi Benjamin Szold, Henrietta Szold (1860–1945), to become the responsible for the publication of the English version of Judaic works and for a contemporary translation in English of the Tanakh. The Jewish Publication Society of America wanted some new or more up-to date language and assembled a committee of translators composed of three professional biblical and Semitic scholars and three rabbis. In 1962 they presented the Pentateuch and seven years later The Song of Songs, Ruth, Lamentations, Ecclesiastes, Esther, and Jonah, where offered all in a single volume for the convenience of synagogue use. It took until 1973 to have the appearance of Isaiah and Psalms.
Language evolving the Jewish community found the revision of the outdated 1917 version New Bible Translation in English for the Jewish People of 1953/1955-1962 also to obsolete and worked on a new version resulting in the “New JPS version“, abbreviated NJPS (it has also been called the “New Jewish Version” or NJV).
The procedure was as follows. The editor-in-chief prepared a draft translation of the entire Torah for the committee. Submitted chapter by chapter with the draft was a considerable body of data consisting, when pertinent, of the renderings of such important older versions as the Septuagint, Targum, Vulgate, and Saadia, and of more recent translations such as Leeser, Revised Version, the 1917 Jewish version, Moffatt, the American (Chicago) Translation, Confraternity, Revised Standard Version, and La Sainte Bible; also the more pertinent comments of such notable exegetes of the Middle Ages as Rashi (d. 1105), his grandson, Samuel ben Meir (Rashbam; d. about 1174), Abraham ibn Ezra (d. 1167), David Kimhi (Radak; d. 1235), Moses ben Nahman (Ramban —Nahmanides; d. about 1270), Levi ben Gershom (Ralbag —Gersonides; d. 1344), and Obadiah Sforno (d. 1550), as well as the works of virtually every modern commentator of merit, Jewish (notably Samuel David Luzzatto—Shadal; d. 1865; and Meir Leib ben Jehiel Michael—Malbim; d. 1879) and Christian. Wherever the draft proposed a new rendering of import, some justification for it was offered. The editor-in-chief usually kept no more than ten or fifteen chapters ahead of the committee, so that he might benefit from the thinking and consensus of his colleagues. {Orlinsky describing the early history of the version in the Introduction of his book, Notes on the New Translation of the Torah (Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society, 1969), pp. 17-19. The New Jewish Publication Society Version}

Harry M. Orlinsky (1908–1992) editor-in-chief of the New Jewish Publication Society (NJPS) translation of the Torah (1962)
Harry M. Orlinsky, Professor of Bible at Hebrew Union College — Jewish Institute of Religion (New York), was asked to serve as editor-in-chief for the new translation, along with H. L. Ginsberg, Professor of Bible at the Jewish Theological Seminary, and Ephraim A. Speiser, Professor of Semitic and Oriental Languages at the University of Pennsylvania, as fellow editors. Associated with them were three rabbis: Max Arzt, Bernard J. Bamberger, and Harry Freedman, representing the Conservative, Reform, and Orthodox branches of organized Jewish religious life. Solomon Grayzel, editor of the Jewish Publication Society, served as secretary of the committee.
Together they created a gender-free translation of the Bible. He also had helped the Protestant National Council with their Revised Standard Version (RSV) of the Bible and then again with the New Revised Standard Version (1989). He was also instrumental in helping to get The Prophets (Nevi’im) (1978) and The Writings (Kethuvim)(1982) published as well.
A number of the changes for the 1985 version had already been projected in Notes on the New Translation of the Torah, edited by Harry M. Orlinsky and published by the Society in 1969 and in the publication of The Book of Job, in 1980. Subsequent research on the text has led to further revisions in the translation of Torah and some revisions in Nevi’im as well.
Afterwards four outstanding Torah scholars (Nahum M. Sarna, Baruch A. Levine, Jacob Milgrom and Jeffrey H. Tigay) with the JPS Torah Commentary series wanted to represent a fusion of the best of the old and new. Utilizing the latest research to enhance their understanding of the biblical text, it came to take its place as one of the most authoritative yet accessible Bible commentaries of our day.
In 1936 “The Holy Scriptures” was published and revised in 1951, by the Hebrew Publishing Company, revised by Alexander Harkavy. In this Hebrew Bible translation in English the Tetragrammaton is presented by the Divine Name of God which is very unusual for a Jewish Bible. Perhaps this accounts for it not gaining the popularity of the JPS Tanakh.

The 1973 edition of the New Oxford Annotated Bible, with the RSV text
In 1962 in-depth academic research from non-denominational perspectives, specifically secular perspectives for “Bible-as-literature” with a focus on the most recent advances in historical criticism and related disciplines, with contributors from mainline Protestant, Roman Catholic, Jewish, and non-religious interpretative traditions, brought a Bible translation that could be used by any Christian or Jewish group. Edited by Herbert G. May and Bruce Metzger, the Oxford Annotated Bible (OAB) study Bible got published by the Oxford University Press (OUP) receiving a a matching edition of the apocryphal books as well as a version of the OAB including them in 1965.
Based on the Revised Standard Version (RSV) of the Bible it was renewed and published in 1973 under the name New Oxford Annotated Bible (NOAB) which got revisions based on the New Revised Standard Version (NRSV) of the Bible of 1989 and got a more ecumenical version in 2000 .

The New Oxford Annotated Bible with Apocrypha: New Revised Standard Version 4th ed. Edition
The New Oxford Annotated Bible with Apocrypha offers a vast range of information, including extensive notes by experts in their fields; in-text maps, charts, and diagrams; supplementary essays on translation, biblical interpretation, cultural and historical background, and other general topics.
Knesset Speaker Kadish Luz announced in 1965 that
“all Presidents of the State of Israel will hereafter be sworn into office on this Bible” (the Koren edition).
The first Hebrew Bible designed, edited, printed, and bound by Jews in nearly 500 years. This Hebrew/English Tanakh Tanakh Yerushalayim (Jerusalem Bible), edited by Koren Publishers Jerusalem was the first Bible published in modern Israel. The Koren Jerusalem Bible (not to be confused with the Catholic translation with a similar title) is a revised version of the Anglo-Jewish Bibles that have been accepted for home and synagogue throughout the English-speaking world. It was published just a few short years before the Six Day War.
 The Chief Rabbinate of Israel accepted The Koren Tanakh for reading the Haftara in synagogues, giving it great importance and authority, quickly gained wide acceptance among many different Jewish communities and became one of the most widely distributed Hebrew editions ever published. It rejects Greek titles, Latin numerals, and chapter divisions based on non-Jewish authority. The English text is divided up according to the traditional system of petuhot (open line divisions) and setumot (closed spaces) as found in ancient Hebrew manuscripts.
The Chief Rabbinate of Israel accepted The Koren Tanakh for reading the Haftara in synagogues, giving it great importance and authority, quickly gained wide acceptance among many different Jewish communities and became one of the most widely distributed Hebrew editions ever published. It rejects Greek titles, Latin numerals, and chapter divisions based on non-Jewish authority. The English text is divided up according to the traditional system of petuhot (open line divisions) and setumot (closed spaces) as found in ancient Hebrew manuscripts. This Koren Tanakh is in English on the left-hand pages and Hebrew on the right-hand pages and names of people and places in the translation are transliterations of the Hebrew names, as opposed to the Hellenized versions used in most translations. For example, the Hebrew name Moshe is used instead of the more familiar Moses. It uses Koren Type, created by typographer Eliyahu Koren specifically for The Koren Bible, and is a most accurate and legible Hebrew type.
This Koren Tanakh is in English on the left-hand pages and Hebrew on the right-hand pages and names of people and places in the translation are transliterations of the Hebrew names, as opposed to the Hellenized versions used in most translations. For example, the Hebrew name Moshe is used instead of the more familiar Moses. It uses Koren Type, created by typographer Eliyahu Koren specifically for The Koren Bible, and is a most accurate and legible Hebrew type.
Since the Koren Tanakh is produced by Jews who believe in the inspiration of Scripture, it remains free from the errors and biases of the ‘New Age’ approach to the Bible. {editor Koren Publishers}
The Bible Society in Israel derived from a phrase in the Book of Jeremiah, in the Hebrew Bible the name Habrit Hakhadasha/Haderekh ( ‘the road’ or the New Covenant) for its paraphrased bible (1976, revised 1991). It uses more basic vocabulary and literary style than does Delitzsch, and is similar to English versions such as the 1966 Good News Bible (GNB), also called the Good News Translation (GNT) in the United States or the Kenneth N. Taylor paraphrasings of 1962 New testament Living Letters and the 1971 “A Thought-For-Thought Translation” The Living Bible (TLB). The Living Bible being the best-selling book in America we can imagine that the Jewish community also wanted a similar Jewish bible.

ArtScroll Tanach Series presenting the comments of the classic giants of ancient and contemporary times in a logical, comprehensible manner, like a master teach on an exciting voyage of intellectual discovery.
 From 1976-1993 work was made to deliver a giant of Jewish versions, the version of choice for Orthodox Jews, and one of the best selling among all Jews, where this publisher is concerned you are spoiled for choice. The rabbinical commentaries are so exhaustive that Mesorah first released their ArtScroll Tanach as 24 volume set. A single volume of all 24 books of the Torah, Prophets, and Writings is presented in one 2,200 page volume, as interpreted by the classic sages of Talmudic and Rabbinic literature, with the Stone Edition of the Tanach.
From 1976-1993 work was made to deliver a giant of Jewish versions, the version of choice for Orthodox Jews, and one of the best selling among all Jews, where this publisher is concerned you are spoiled for choice. The rabbinical commentaries are so exhaustive that Mesorah first released their ArtScroll Tanach as 24 volume set. A single volume of all 24 books of the Torah, Prophets, and Writings is presented in one 2,200 page volume, as interpreted by the classic sages of Talmudic and Rabbinic literature, with the Stone Edition of the Tanach.
In 1981 Moznaim Publishing The Living Torah by the American Orthodox rabbi and author known for his knowledge of physics and kabbalah, Aryeh Kaplan offered an Orthodox translation into contemporary English. He includes the rabbinic elucidation of the text, which he consciously interspersed with later rabbinic commentary and Jewish law. It was reissued in a Hebrew-English version with haftarot for synagogue use. After Kaplan’s death in 1983, The Living Nach was translated in the same style by Yaakov Elman for Nevi’im (two volumes: “The Early Prophets” and “The Latter Prophets”) and Ketuvim (“Sacred Writings” in one volume) by Moshe Schapiro, M.H. Mykoff (Breslov Research Institute), and Gavriel Rubin.
Inspired by the German translation prepared by the Austrian-born Israeli Jewish philosopher, honorary professor at the University of Frankfurt am Main, Martin Buber and the German Jewish theologian, philosopher, and translator Franz Rosenzweig, Everett Fox translated the Torah (The Five Books of Moses, 1995) for Schocken Press. It uses hyphenated phrases and is printed in blank verse, and the personal and place names are transliterated versions of the Hebrew names.
In 2005 appeared Jay P. Green’s The Interlinear Bible: Hebrew-Greek-English (Peabody, Mass.: Hendrickson Publishers) based on the Masoretic text. The words are keyed to Strong’s Exhaustive Concordance. The print is much smaller than John R. Kohlenberger III, Interlinear NIV Hebrew-English Old Testament (based on the Hebrew text of BHS and the NIV) But the Green translation does seem not as accurate. Volume also contains a Linear Greek New Testament.
Rudolf Kittel’s Biblia Hebraica, the Dead Sea Scrolls and the Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia were used as a basic for several Jewish translations and also used for the 1995 revision of the American Bible, maintaining a word-for-word translation style, presented by the Lockman Foundation as the New American Standard Bible, which is widely regarded as the most literally translated of major 20th-century English Bible translations. A committee consisted of people from many Protestant, predominantly conservative, denominations, Presbyterian, Methodist, Southern Baptist, Church of Christ, Nazarene, American Baptist, Fundamentalist, Conservative Baptist, Free Methodist, Congregational, Disciples of Christ, Evangelical Free, Independent Baptist, Independent Mennonite, Assembly of God, North American Baptist, and “other religious groups” prepared the original work (1963-1971) and more than 20 individuals worked on modernizing the NASB in accord with the most recent research, supplanting the 1977 text in current printings, save for a few (Thompson Chain Reference Bibles, Open Bibles, Key Word Study Bibles, et al.) It got further revisions from 1992 up to 1995.
Early this century Robert Alter translated the Torah in The Five Books of Moses (2004) and in a Chasidism translation created the Gutnick Edition of the Chumash (2006).

16th-century depiction of the French religious scholar Rashi, acronym of Rabbi Shlomo Yitzḥaqi (1040-1105) renowned medieval French commentator on the Bible and the Talmud
Judaica Press, an Orthodox Jewish publisher, has published a multi-volume bilingual Hebrew–English translation of the Bible that includes the medieval French rabbi Rashi‘s comprehensive commentary on the Talmud and commentary on the Tanakh in both Hebrew and English, Complete Tanach with Rashi.
Although the Pentateuch has not been fully published in hardcopy (Genesis [in three volumes] and Exodus [in two volumes] only), Judaica Press also published a set of 24 bilingual Hebrew–English volumes of Mikraot Gedolot for Nevi’im and Ketuvim, published as Books of the Prophets and Writings. As in traditional Mikraot Gedolot, the Hebrew text includes the masoretic text, the Aramaic Targum, and several classic rabbinic commentaries. The English translations, by Rosenberg, include a translation of the Biblical text, Rashi’s commentary, and a summary of rabbinic and modern commentaries. {Free Encyclopedia Wikipedia}
The Jewish Annotated New Testament, Edited by Amy-Jill Levine and Marc Z. Brettler
In 2011 University Professor of New Testament and Jewish Studies Amy-Jill Levine, E. Rhodes and Leona B. Carpenter Professor of New Testament Studies, Vanderbilt Divinity School, and Marc Z. Brettler, Dora Golding Professor of Biblical Studies, Brandeis University, edited The Jewish Annotated New Testament. It brings out Jewish background of early Christianity, New Testament writers and can be very helpful for non-Jewish readers interested in the Jewish roots of Christianity, also making it clear where certain Christians went wrong in their thinking because of their insufficient knowledge of Jewish way of speaking and thinking. The book also explains Jewish concepts (e.g., food laws, rabbinic argumentation) for non-Jews, Christian concepts (e.g., Eucharist) for Jews.
***
***
***
*
Please find to read
- Magil’s linear school Bible, by Joseph Magil. Hebrew text and English translation … The five book of Moses.
- Magil’s linear school Bible
- Magil’s linear school Bible, or, The Hebrew Bible in its original language : self taught for teachers and students . . . : a new and easy method for popularizing the study of the original Hebrew Bible by means of a linear translation – Archive copy Robarts – University of Toronto
- Magil’s linear school Bible or The Hebrew Bible in its original language self taught for teachers and students, ., a new and easy method for popularizing the study of the original Hebrew Bible by means of a linear translation *EBOOK*
- Leeser’s Jewish Bible (1853)
- The twenty-four books of the Holy Scriptures, carefully translated according to the Massoretic text, on the basis of the English version, after the best Jewish authorities and supplied with short explanatory notes by Isaac Leeser
- Isaac Leeser: The Right Man at the Wrong Time
- The New Jewish Publication Society Version
- Samuel ben Meir (Rashbam)
- Rabbi Samuel Ben Meir (Rashbam): A Short Bio
- Jerusalem Bible (Koren)
- Full text of “Oxford Annotated Bible Revised Standard Version -(R.S.V.) 1952“
- Living Nach – Sacred Writings
- New JPS+ Mari
- Online reading of: The Living Torah
- The Complete Tanach with Rashi’s Commentary
- Stone Edition of the Tanach.
+
Preceding articles:
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #1 Pre King James Bible
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #2 King James Bible versions
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #3 Women and versions
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #4 Steps to the women’s bibles
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #5 Further steps to women’s bibles
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #6 Revisions of revisions
++
Additional reading
- Written and translated by different men over thousands of years
- Lord in place of the divine name
- Lord or Yahuwah, Yeshua or Yahushua
- Lord and owner
- People Seeking for God 7 The Lord and lords
- Accuracy, Word-for-Word Translation Preferred by most Bible Readers
+++
Further reading
- The Jewish Bible ≠ The Old Testament
- New JPS Commentary Volumes, Now in Accordance
- Your Life Without Torah
- From the Desk of Kenneth Seeskin
- From the Desk of Alan Levenson
- From the Desk of Zev Eleff: A Touchy Subject
- Torah on Tap; the Tragedy of Leadership
- The Jerusalem Debate – Eleven Objections and Responses | The Lamb’s Servant
- 613 Mitzvot & Yeshua keys to be Nazarene Jews
- Shabbat Lekh L’kha: Go Forth, in Jewish
- We Need A Word Make-Over
- The Completely Not-Boring History of the Bible, part 1
- Israel: Does the Hebrew Bible indicate the Messiah, the Anointed One of the House of David, is divine?
- Israel: According to the Hebrew Bible did the Lord ever become a man
- Did Avraham keep all Torah Mitzvot?
- Yom Teruah
- More on English Bible Versions
- Sermon: A Man Who Gave His Life that You Might Have an English Bible
- Dr. John Wyclyffe, Low-Tech Bible Translator
- Williams Tyndale: The Experiential Outworking of Sola Scriptura
- Was Dr. John R. Rice a Heretic?
+++
Related articles
Related articles




























 It was after 25 years serious research that in 1881 the British bishop, biblical scholar and theologian, and
It was after 25 years serious research that in 1881 the British bishop, biblical scholar and theologian, and 










 It was his successor as society president,
It was his successor as society president, 
 Already around the turn of the 18th to 19th century women had started wanting to have a stronger voice in the education of children. Also parents started looking more at how to bring up children together in a community. They had seen the public school system starting to develop going away from certain ways of life preferred by them. The spiritual aspect was important and could not be forgotten. Discontented with the new public school system more
Already around the turn of the 18th to 19th century women had started wanting to have a stronger voice in the education of children. Also parents started looking more at how to bring up children together in a community. They had seen the public school system starting to develop going away from certain ways of life preferred by them. The spiritual aspect was important and could not be forgotten. Discontented with the new public school system more 

 The Bible was also published in several languages by Elias Hutter (Nuremberg, 1599-1602), and by Christianus Reineccius (Leipsic, 1713-51). Ten years before the “Polyglot Bible in eight languages” (2 vols., London, 2nd ed. 1874) the
The Bible was also published in several languages by Elias Hutter (Nuremberg, 1599-1602), and by Christianus Reineccius (Leipsic, 1713-51). Ten years before the “Polyglot Bible in eight languages” (2 vols., London, 2nd ed. 1874) the  In this Interlineary literal Word for Word English translation ‘Signs of Emphasis’ were given; whilst under each Greek word the English equivalent is printed. In the slim right-hand column of each page is presented a modern English translation as made by Benjamin Wilson. Also a copious selection of ‘References’; many appropriate, illustrative, and exegetical ‘Foot-notes’; and a valuable ‘Alphabetical Appendix’ are given. This combination of important items could not be found in any other book at that time.
In this Interlineary literal Word for Word English translation ‘Signs of Emphasis’ were given; whilst under each Greek word the English equivalent is printed. In the slim right-hand column of each page is presented a modern English translation as made by Benjamin Wilson. Also a copious selection of ‘References’; many appropriate, illustrative, and exegetical ‘Foot-notes’; and a valuable ‘Alphabetical Appendix’ are given. This combination of important items could not be found in any other book at that time. Bible students form the Zion’s Watchtower suggested that,
Bible students form the Zion’s Watchtower suggested that,

















 Bijbelvorsers Webs
Bijbelvorsers Webs Belgische Vrije Christadelphians / Belgian Free Christadelphians – Old Google Main Website
Belgische Vrije Christadelphians / Belgian Free Christadelphians – Old Google Main Website Christadelphian Ecclesia
Christadelphian Ecclesia Hoop tot Leven – Redding in Christus
Hoop tot Leven – Redding in Christus
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #9 Restored names and Sacred Name Bibles
In the previous chapter we showed that in the 1980ies and 1990ies publishers looked for way to have some cheap material easily printed and reproduced. For them the Word of God or the Bible looked very handy to use, because when they changed here and there some words they could publish it freely without having to bother about copyrights. In those years lots of economical and political problems started showing up, the Gulf War and beginning pressure from Islamic terrorist groups, making that people went looking for alternatives and solutions for making their life better.
From the time that all sorts of translations were provided for different groups of people, like housewives, prisoners, blue-coloured workman, modern women and modern man – Good News for modern man New Testament in Today’s English Version
Many publishers knocking the ball around presented booklets, pocket editions but also hard-covers with fragments and with full texts of the Bible. Many wanted to bring out a ‘fresh’ or ‘up-to-date’ Bible translations which could draw on a particular group of people or could be favoured by a particular denomination. For some it did not matter so much when the words got twisted a little-bit or when the translation was so loosely done it went very far from the original Holy Writings. The Good News Bible, which also presented a version for the ‘modern man’ is such a Bible translation were too much liberty is taken, but which manage to continue to exist until today.
The Liberator (2006) a retelling of the life of Jesus based on the gospels Matthew, Mark and Luke, could find perhaps a prolonged life because of the Lacey Theatre Company toured shows based on this book in 2007 and 2008, and extracts also being performed in “St David’s Praise” (31 May 2008, St David’s Hall in Cardiff).
Titlepage and dedication from a 1612-1613 King James Bible, printed by Robert Barker. (Photo credit: Wikipedia)
Coming closer to the 400th birthday of the publication of the Authorised King James version, several companies also started bringing new King James Versions, whilst others found it time to not only update the language but to restore the names and present the words like it would be linguistic right.
Some of the new King James versions around the turn of the century did not alter the language much, like the minor very conservative update of the King James Version, the 21st Century King James Version bible, which stays true to the Textus Receptus and does not delete Bible passages based on Alexandrian Greek manuscripts. Obsolete and certain archaic words are eliminated but further it preserves the traditional Biblical language, making it possible to have all those using a King James Bible to follow easily. The 21st Century King James Version has also been released in an edition with the Apocrypha and without the unusual formatting; this is known as the Third Millennium Bible.
Having taken 7 years to complete the New King James Version (NKJV) already commissioned in 1975, published by HarperCollins (a subsidiary of News Corp), conceived by Arthur Farstad with 130 biblical scholars, pastors, and theologians, alters the language more significantly from the 1611 King James Version, but still trying to retain the purity and stylistic beauty of the original.
The exceptionally rich and accurate translation of the Holy Scripture became first available in 1982 but got more in the picture around the 400th birthday of the original KJV, also receiving some new study edition.
The NKJV claiming to be “more accurate” because it leaves untranslated words like “Gehenna,” “Hades” and “Sheol” is misleading the people and has the only reason not to bump some church-member’s head. They choose for security not to knock against those who keep insistently wrong teachings of having gehenna/hades/sheol being a place of doom, the hell, where so called sinners would be penalised for their sins, instead of an abode of the dead, the grave/tomb. For that reason also many present bibles are afraid to print the Divine Name of God (יהוה) where it stood in the original writings, because also there people would come clearly to see about whom is been spoken and soon would come to see the difference between Jehovah God and Jehovah God His only begotten beloved son, יהושׁע Jeshua, where all of those KJV’s print Jesus.
But some of the newer versions restored the names. By them avoiding, where most trinitarians loved to see “Lord“, having titles placed instead of the original names, using the names of the people makes it much clearer for the bible reader about whom is been spoken, and as such mistaking one person fro the other is avoided. This way the Restored Name Versions and the New European Version are King James versions which haven taken up the old way of presenting God’s Name like it was in the original King James version, to leave no doubt when is spoken about the God of gods or about the son of God.
For the English Bible translations God’s Divine Name was already in the William Tyndale Bible of 1530 and in the King James Version in 1611. The excuse of avoiding the risk of taking God’s name (יהוה/YHWH) in vain, according to devout Christians was not necessary any more, because Jeshua liberated us from the curse of sin and restored the relationship between God and man. After the sacrifice of God‘s only begotten son, man does not have to be afraid any more to come up to God and speak to Him using His Sacred Name. Being convinced of the restored relationship and feeling that we as children of God not only may use His Name but should spread His Name, several Sacred Name Bibles started seeing the light.
When we look at the original texts and see how frequent that Divine Name appears, and hear how God speaks about His Name, we should comprehend its importance. The Tetragrammaton occurs 6,828 times in the Hebrew text (BHK and BHS). This is confirmed by the Theologisches Handwörterbuch zum Alten Testament, Vol. I, edited by E. Jenni and C. Westermann, 3rd ed., Munich and Zurich, 1978, cols. 703, 704. The New World Translation renders the Tetragrammaton as “Jehovah” in all occurrences.
The knowledge of the correct pronunciation of God’s name was there at the time of Christ, as it was heard at least by the high priest until 70 CE and respectively its utterance was common practice until at least the 1st century CE, but Hebrew speaking people can and do read the name in some groups as well as the majority of Messianic Jews who also accept that the relationship between God and man is restored by the Mashiah or Messiah.
The Jerusalem Bible: Reader’s Edition Hardcover – Abridged, February 15, 2000
Though throughout history there have been several versions which used God’s Name Jehovah or placed Yahweh for the Tetragrammaton, like The Jerusalem Bible (JB or TJB) (translated from the French La Bible de Jérusalem of 1956, revived and updated in 1973), first introduced to the English-speaking public at the time when the fear for the users of God’s Name (the Jehovah Witnesses started growing) in 1966 and published by Darton, Longman & Todd. As a Catholic Bible, it includes the traditional 73 books found in most English translations until the mid 19th century: the 39 books shared with the Hebrew Bible, along with the seven deuterocanonical books as the Old Testament, and the 27 books shared by all Christians as the New Testament. It also contains copious footnotes and introductions. It is the basis of the Lectionary for Mass used in Catholic worship throughout England, Wales, and the majority of the English-speaking world outside the United States and Canada, though the Catholic Bishops’ Conference of England and Wales has approved other translations for conditional liturgical use.
The New American Bible (With the Revised Book of Psalms and the Revised New Testament) New American Bible Revised ed. Edition by World Bible Publishing St
For the dioceses of the United States and the Philippines the New American Bible (NAB) Catholic Bible translation first published in 1970 is used, also being approved by the Episcopal Church in the United States. The spelling of proper names found in this edition departs from the ones found in older Catholic Bible versions, such as the Douay, and instead adopts those commonly found in Protestant Bibles.
The Revised New American Bible (RNAB) had the traditional phraseology — absent from the 1970 edition — restored to the New Testament, and having several non-traditional gender-neutral terms incorporated in its 1986 version. The New Testament was almost completely revised, and bears a much closer resemblance to the 1941 Confraternity version, as opposed to the much more periphrastic 1970 NAB NT. In 1991 the Book of Psalms was amended to introduce the use of extensive gender-neutral language. The last update is from 2011, including the newly revised Old Testament and re-revised Psalms, and the revised New Testament from the second edition.
Several English people did not like it that God’s Name was printed and would have preferred the Name of God be left unpronounced, or substituted with Lord or another title. In 1985, the English translation was completely updated. This new translation — known as the New Jerusalem Bible (NJB) — was freshly translated from the original languages and not tied to any French translation any-more (except indirectly, as it maintained many of the stylistic and interpretive choices of the French Jerusalem Bible).
When the the Catholic Truth Society in 2007 published the CTS New Catholic Bible, consisting of the original 1966 Jerusalem Bible text, prepared by the faculty of the Dominican Biblical School in Jerusalem, on the basis of the Hebrew and Greek and revised to match its use in lectionaries throughout most English-speaking countries, in conformity with the directives of the Congregation for Divine Worship and the Discipline of the Sacraments and the Pontifical Biblical Commission the name “Yahweh” was replaced by “the LORD” throughout the Old Testament, which frequently departs from the traditional Masoretic text, and the Psalms have been completely replaced by the 1963 Grail Psalter. The revised text is accompanied by new introductions, and textual and liturgical notes, supplemented as needed with material from the notes to the New Jerusalem Bible.
(Hebrew names are also used where possible for annual festival days, as well as being used, minimally, for ambiguous words).
For many english people accustomed to the KJV order of books it may demand some adaptation to come used to the original order of the Tanakh (Old Covenant Scriptures) which is restored according to the order of the Hebrew Scriptures, i.e. Torah, Neviim, Kethuvim. In the newer versions the New Covenant Writings (Brit Chadasha / New Testament), its allusions to the Tanakh are printed in Bold, and cross referenced to the Tanakh (Old Covenant Scriptures).
Dr. Chris J. Koster, with the aid and support of other scholars and textual experts from both Jewish and non-Jewish backgrounds in different parts of the world, was the original translator for the South African and English version. He formed the ISR so that it could continue the work, even after his death (+4 May 1995). At the ISR, which also publishes the Hebraic Roots Version Scriptures (HRV), the board of directors is now overseeing the on-going work of translation and revision. It was around the time of his death that brother Marcus Ampe got to know him and his work and asked if he could make a Dutch version of the work. He had requested the version in Afrikaans, but never got it. The text fragments from 1993/1995 he got and 1998 had some little differences with the 2009 and 2010 versions. (At the moment in the ecclesia we use the 1998 and 2010 version, next to the NWT and the Bible Students Reference bible.) Because of his daily work and Marcus Ampe writing for several websites the translation-work got very much slowed down, also by his work on the Christadelphian modules for the Online Bible program.
Don Esposito, Senior Elder of the Congregation of YHWH Jerusalem, for his Hebrew Roots Version used the original names of our Creator, but presented it from the Paleo Hebrew as YAHWEH (יהוה HWHY/YHWH), and for God’s Son, our Saviour he used Yahshua (יהושׁע Yeshua/Jeshua in modern spelling), throughout. Because there was no letter J at that time he kept to the Y. Though than you also could say there did not exist a letter u and still should use the v or also for the w one still should, in that instance use, the vv. We do know also in the Catholic Imprimatur Bibles from the 1950ies there was written Yehowah, but in later prints this became modernised to Jehovah. The “New Testament” portion is titled “The Ketuvim Netzarim” (“Writings of the Nazarenes”) and is also a Messianic Sacred Name Edition and is translated from the original Aramaic and Hebrew. The NT books are also in the original manuscript order (The Gospels; Acts; James, 1&2 Peter; 1,2,3 John, Jude; Pauline Epistles; Revelation) but the titles of the books are their Hebraic names. The HRV also divides the books into two sections The B’sorah (Goodnews) and The Sh’lukhim (Emissaries).
The HRV Complete Bible is by many considered to be the first complete Messianic Study Bible.
Further there where Ted Ramp, President of Halleluyah Scriptures Inc. (Incorporated Dec. 6, 2012) – Fort Wayne, IN, Robin Ramp, Secretary of Halleluyah Scriptures Inc. , Erik Klausner, Marilyn Nave and Nance Whitaker who seem to have broken with Deborah (Debra) and Ken Allen and their the Halleluyhah Scriptures.
This has taken years of research as it is not always obvious that English words are derived from pagan deities. Much diligent research has been done into assuring that there are no pagan words used to describe our wonderful Father and His Son and as such we also do not find the false name of the Messiah which was given in the 4th century to the rabbi, but which is now the common name, Jesus, coming from Issou or Hail Zeus. In this version all paganism and names of false gods that have traditionally been used in translation when pertaining to the the Father, His Son and His people have been avoided, and in many cases retain a Hebrew transliteration if the word is linked to paganism, though we do find some words which are still presented like a name, like Satan, though in the Name Meaning guidebook they print it right giving the reading the real English word ‘adversary’. The reason they probably did not translate it this way in their translation is perhaps some of their translators do want to believe in a devilish figure, called ‘Satan‘ instead of heaving any adversary being called so.
Although the English language is replete with words derived from pagan deities, this translation has attempted to remove most, if not all of these words when attributed to the Almighty, His Son or His people. Problem for translators is that certain words or Hebrew terms have no comparison in English.
HalleluYah Scriptures chose to retain the Hebrew term “qodesh” for ‘holy’ or ‘set-apart’ (for we are qodesh and not Set apart from Him), and removed all occurrences of the word “set” in obedience to the Word (Exodus 23:13, Josiah 23:7, Psalms 16:4). eg.
qodesh vs set-apart*
Qadosh One vs Set-apart One*
qodeshi vs set-apart one*
qodeshim vs set-apart ones*
qodeshah vs set apartness*
put vs set*
depart vs set* out
lit vs set* (on fire)
In the HalleluYah Scriptures you may find Ruaḥ ha’Qodesh vs Set-apart Spirit, Ruaḥ vs Spirit and Ruaḥoth vs Spirits.
For the Messiah/Mashiah/Masschiah, to maintain the Hebrew origin of many words borrowed from the Greek texts, HalleluYah Scriptures used the Hebrew words in the following Mashiaḥ vs Messiah, Mashiaḥiyim vs Messianic, talmidim vs taught ones, Gĕy-Hinnom vs Gehenna, Shabbath vs Sabbath and Shabbathoth vs Sabbat.
Because the title Master is linked etymologically with the goddess Maia through the common root word “Meg” the original Hebrew form of Adonai used in the Hebrew scrolls is used as the title for the Almighty. Some people teach that Adon is a pagan word based on the greek false god Adonis. But the Hebrew is the original form where as Adonis is just a copy used for wicked means. It does not mean the word Adonai is pagan.
HalleluYah Scriptures uses the words on the left.
Pesaḥ vs Passover
Matstsoth vs Unleavened Bread
Shaḇuoth vs Weeks
Yom Teruah vs Trumpets
Yom Kippurim vs Atonement
Sukkoth vs Booths
Yoḇĕl vs Jubilee
LIFE vs. HAI
Although there are a few situations where the context or root word may be translated with an ‘added’ word, HalleluYah Scriptures chose to remove as many as physically possible while maintaining a coherent translation. Space does not permit the number of italicized words that were removed and/or reworded, but amounts to well over 80% from the total of added words.
In many cases this required re-writing an entire verse to conform with the original language and this was not an easy job taking many months. The HalleluYah Scriptures translation team are working on the other 20% of added words and will make the changes in following print runs when completed.
This will aid many people who do not believe that our Saviour was the promised Redeemer of Yisrael/Israel. This book will prove without a shadow of a doubt that Jeshua (Jesus Christ) is the Saviour.
***
You may visit the HalleluYah Scriptures web site and read more about this important project that has touched and changed thousands of lives forever. http://www.Halleluyahscriptures.com
***
No Footnotes, No Explanatory References, No Doctrines of Man! Just the Word of YHWH…
HalleluYah Scriptures Paralell Hebrew Bible & Messianic Prophecies Fulfilled New Book
***
The Christadelphians have also some projects where a restored name version is sent out to those who want to read the word of God, so that it can be as a lamp to man’s feet and a light to our path, Psalms 119:105; 2 Peter 1:19. They have “The Scriptures” with the tetragrammaton and God’s Name Jehovah in it, but also distribute two older King James versions (with Jehovah) and a new King James version with the (transcribed) name Yahweh in it.
New European Version of the Bible with commentary
The New European Version of the Bible is a remediation of the King James Version into modern English, correcting some glaring issues in translation here and there. The NEV Bible is published in hard copy with a brief commentary on a few verses from each chapter, printed at the bottom of each page. At the back of the volume, there is a reduced version of the book Bible Basics. There is also an online version provided which has a dedicated page for each chapter of the Bible. On each page there is the Bible text, basic commentaries and links to other resources relevant to that chapter. There is also a “Deeper commentary” tab on each chapter. This gives some deeper insights on some Old Testament chapters; and in the New Testament, this tab connects to the New European Commentary. This is an in-depth, verse by verse commentary on the entire New Testament.
Duncan Heaster
Duncan Heaster
The NEV is published by Carelinks Ministries who say to pray earnestly that this Bible and the distribution of it will play a part in the spreading of the Gospel worldwide before Christ returns. Though also for this editor we must give a warning.
They say they are Christadelphian, but out of experience we have found that they do not take on a Christian attitude, namely not willing to share brotherly love with each other. We do have the impression it is more a cult organisation around one ex-communicate Christadelphian preacher, Duncan Heaster who has written over 20 books and having edited “Gospel News” magazine for over 20 years, has a team of followers round him, who do a lot of great work, but once people get baptised in their organisation they do not want them to have contact with others. They do not want their members to share with other Christadelphians or Bible students. So please if you order a copy by them and would become interested in what they teach and want to get baptised, never forget those who brought you into contact with them.
***
Free Bible Distribution, New European Version Free Bible with commentary
***
*
Find a.o.
+
Preceding articles:
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #1 Pre King James Bible
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #2 King James Bible versions
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #3 Women and versions
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #4 Steps to the women’s bibles
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #5 Further steps to women’s bibles
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #6 Revisions of revisions
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #7 Jewish versions
Old and newer King James Versions and other translations #8 Selective Bibles and selective people
Building up the spirit of the soul
A fact of History or just a fancy Story
++
Additional reading
+++
Further reading
+++
Related articles
Rate this:
Share this:
Category:
Bible Students, Bible study, Christadelphian, God Jehovah Yahweh (English), History, Jesus Christ, Jeshua Messiah, Religion, Video, Word of God
Tagged with: